UTP Cables
UTP Cables
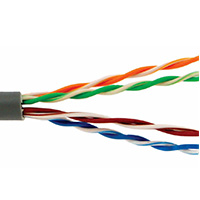
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP), is by far the most common structured cable type that consists of two unshielded wires twisted around each other. Due to its low cost, UTP cabling is used extensively for local-area networks (LANs) and telephone connections. UTP cable is used not only for networking but also for the traditional telephone (UTP-Cat 1). There are different types of UTP categories and, depending on what you want to achieve, you would need the appropriate type of cable. UTP-CAT5e is the most popular UTP cable which came to replace the old coaxial cable that was not able to keep up with the constant growing need for faster and more reliable networks.
There are six different types of UTP cable designed for different applications, including telephone, computer network and ethernet applications from 1 Mpbs, for traditional telephones, to 1000 Mpbs for gigabit ethernet. UTP cable typically uses copper wire. The various types of UTP, called CAT1, CAT2 and so on to CAT6, specify the exact type of wire, jack, the twist in the wires and the quality of the connection.
Unshielded wires don’t rely on grounding to the same extent as shielded cabling. This improves reliability and decreases the amount of time it takes to install them. If you forgo STP wiring, you needn’t ground each cable at both ends. Don’t choose shielded cabling unless you’re willing to perform all of the necessary grounding tasks. An improperly grounded shield collects signals; it actually worsens crosstalk and electromagnetic interference. In this situation, you’d have better results with UTP wiring.
Unshielded wiring weighs comparatively little. These cables are substantially more flexible and have compact dimensions as well. Such advantages make UTP products less difficult to install, transport and maintain. They’re versatile and able to fit in rather small spaces. You can thus pull more unshielded wires through a narrow passage or conduit. However, keep in mind that crosstalk could become a problem. The limited size and weight of UTP cables decrease their expense because they cost less to ship, thus suppliers save money on transportation as well as packaging materials.
Showing the single result